
What is a nontactile membrane switch? Non tactile meaning
What is a nontactile membrane switch? Non tactile meaning
Nontactile membrane switch is a membrane switch that provides almost no physical feedback when operated, and the user can hardly feel the tactile change when pressing. This design is common in modern home appliances and industrial equipment, and is suitable for scenarios that require a simple operating interface and a quiet environment.

What is a membrane switch?
Membrane switch is a low-profile electrical switch built with flexible layers. When pressed, it closes a circuit and sends a signal. Instead of traditional mechanical parts, it relies on pressure between thin films.
Most membrane switches are made up of four main parts: a graphic overlay, a top circuit layer, a spacer, and a bottom circuit layer.
They’re found everywhere—from home appliances and industrial panels to medical devices and control systems. Their appeal lies in their slim design, long life, and moisture resistance. These switches are also sealed tightly, which keeps out dust, dirt, and liquids.
Because they are flat and easy to customize, membrane switches are a favorite in industries that need clean design and reliable performance. They are also budget-friendly, especially in bulk production.
What does non-tactile mean?
Non-tactile means there’s no physical feedback when the button is pressed. You won’t feel a “snap” or “click.” The press is silent and smooth.
In a nontactile membrane switch, the user presses a flat surface that registers input without providing sensory confirmation. That might sound like a drawback, but in many applications, it’s a huge benefit.
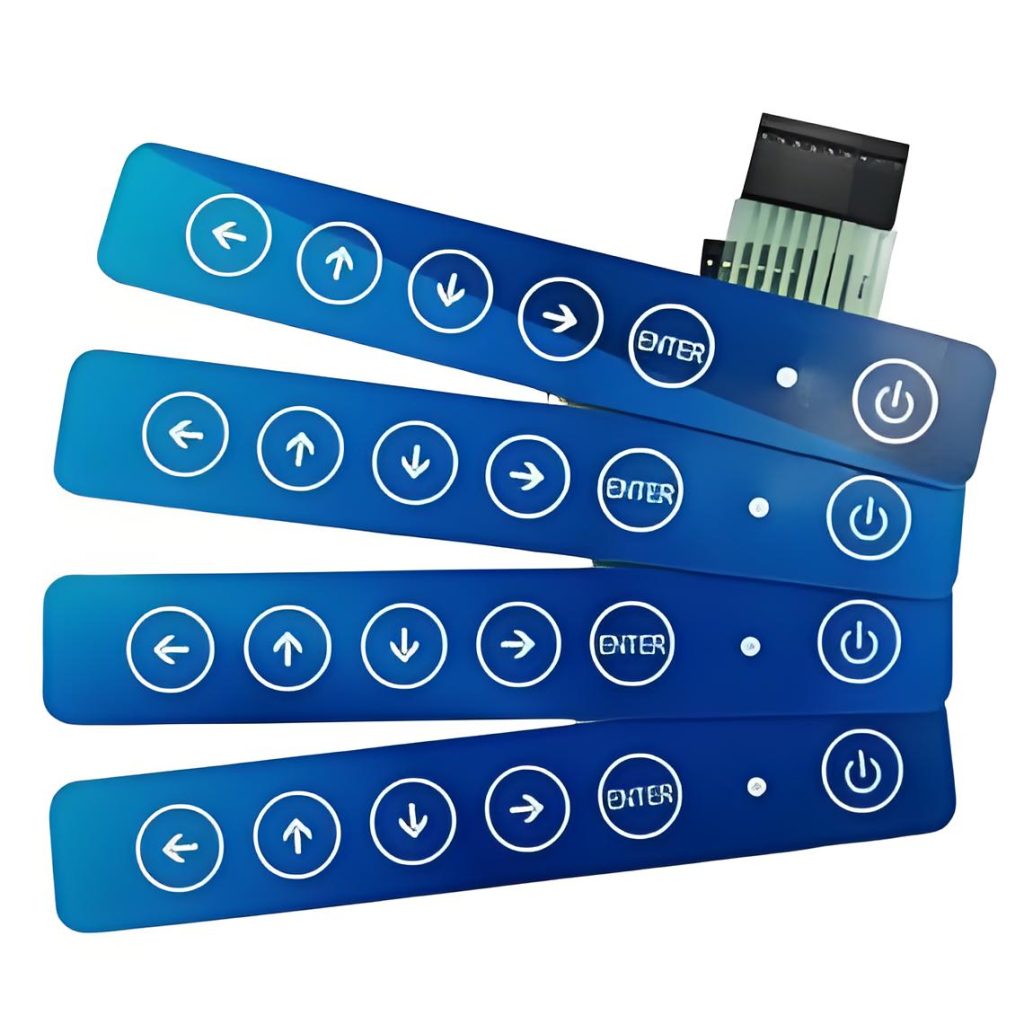

Non-tactile switches have fewer moving parts, so they last longer. They’re quieter. They’re easier to clean. And they make it easier to build fully sealed surfaces.
The term non tactile literally means “without touch feedback.” This doesn’t mean the switch doesn’t work. It just means it doesn’t respond with a physical sensation.
What is the difference between tactile and non-tactile switches?
The difference lies in what the user feels during actuation. Tactile switches give a physical response—a sharp click or snap. They usually have a metal dome or other feedback mechanism beneath the surface. When pressed, the dome collapses and provides a “bump” that confirms input.
In contrast, nontactile membrane switches are flat. They don’t include a dome. So when the user presses, the switch registers the input silently, without feedback.
Tactile switches are great when feedback matters. They’re helpful in low-light environments or high-pressure jobs, where operators need to feel every input.
But tactile domes have their drawbacks. They add cost, wear out faster and are more complicated to clean.
Nontactile switches are better in settings where the user doesn’t need physical confirmation. These switches offer a longer lifespan, cleaner surfaces, and lower cost.
What is the difference between momentary and tactile switches?
It’s easy to confuse momentary switches with tactile switches, but they refer to two different things.
Momentary describes the function. The switch stays on only while it’s pressed. Once the pressure is removed, the connection opens again.
Tactile, on the other hand, describes the feel. A tactile switch responds with a snap or click when activated. It gives the user a clear signal that the button worked.
Switch can be both momentary and tactile. It can also be momentary and non-tactile.
If you want physical feedback and short activation time, you’ll want a tactile momentary switch. If you need a smooth press with silent performance, a nontactile momentary switch is ideal.
What are the different types of membrane switches?
Membrane switches come in many types, depending on function, feedback, and design goals.
- Tactile membrane switch:
This switch includes a dome under the surface. It gives the user a clicking sensation when pressed. The tactile feedback is clear, making it useful in interfaces where speed and certainty matter.
- Nontactile membrane switch:
This type has no dome. Pressing the surface sends the signal without any snap. It’s smooth, simple, and better for quiet or hygienic environments.
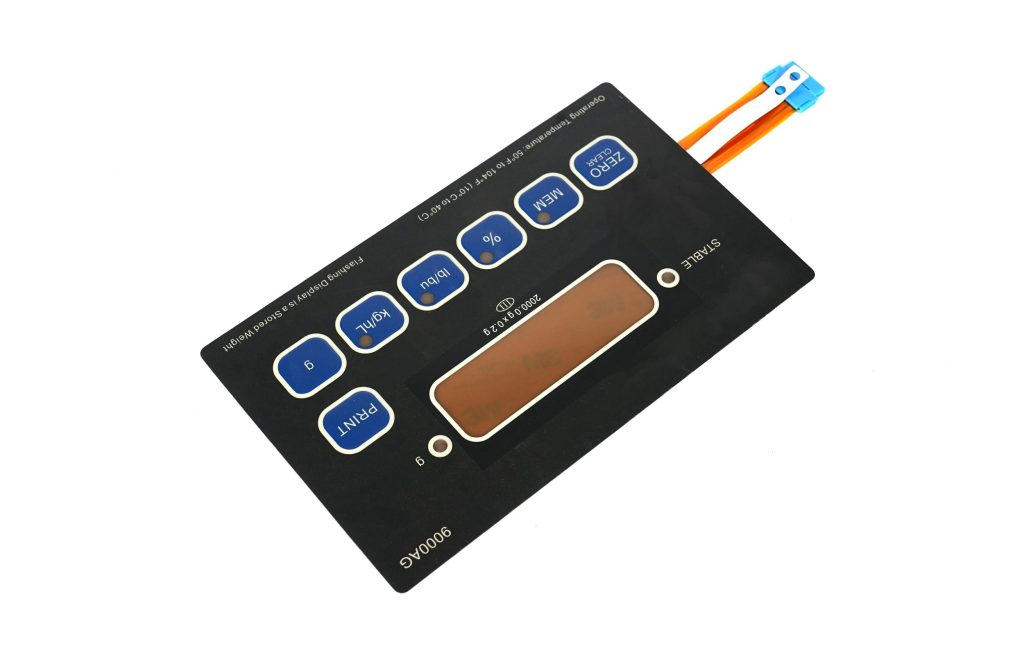

These use LEDs or fiber-optics to light up the interface. That helps users in dark or low-visibility conditions. It adds a modern touch too.
- Capacitive membrane switch:
These switches respond to human touch using the body’s natural conductivity. They don’t require pressure. This technology is used in smartphones and touch panels.
- Hybrid switches:
Some switches combine tactile feedback with backlighting or capacitive sensing. These custom builds are used in advanced applications.
Instead of printed film, the circuit is etched into a printed circuit board (PCB). This makes it stronger and allows for complex connections.
Choosing the right type depends on the needs of the user and the environment. Each switch brings different strengths, and knowing the options helps improve performance.
What role does a spacer layer play in a membrane switch?
The spacer layer is critical in any membrane switch design. It keeps the top circuit and bottom circuit apart until the button is pressed.
Without the spacer, the switch could short out or stay “on” unintentionally. The spacer makes sure the circuits connect only when needed.
In nontactile membrane switches, this layer becomes even more important. Since there’s no dome to push the top layer back, the spacer helps reset the switch after each press.
It also ensures the correct travel distance. That means more consistent actuation across the entire keypad or panel.
The spacer is usually made of polyester or adhesive film. It includes holes or cutouts where the contact should happen. This gives engineers precise control over the switch’s response and performance.
Good spacer design improves:
- Accuracy
- Longevity
- Durability
- Speed of return
It may not be the most visible part, but the spacer is essential to a smooth user experience.
What is the difference between membrane and tactile switches?
This can be confusing because “tactile” is a description of feeling, while “membrane” refers to structure.
A membrane switch is a type of switch that uses thin layers to create circuits. It’s about how the switch is made. It can be tactile or non-tactile.
A tactile switch is about the user’s experience. It provides a click or snap. But not all tactile switches are membrane switches. Some are mechanical. Some use rubber domes. Others use metal domes.
So, you can have:
- Tactile membrane switches (with domes)
- Nontactile membrane switches (without domes)
- Mechanical tactile switches (like keyboard switches)
If feedback is critical, go tactile. If you want sleek, flat, durable input, go with a non-tactile membrane design.
What is the difference between a microswitch and a membrane switch?
A microswitch is a mechanical device with a lever or small actuator. It operates with a quick movement and a clear click. These are often found in safety systems, appliances, and equipment that requires solid mechanical action.
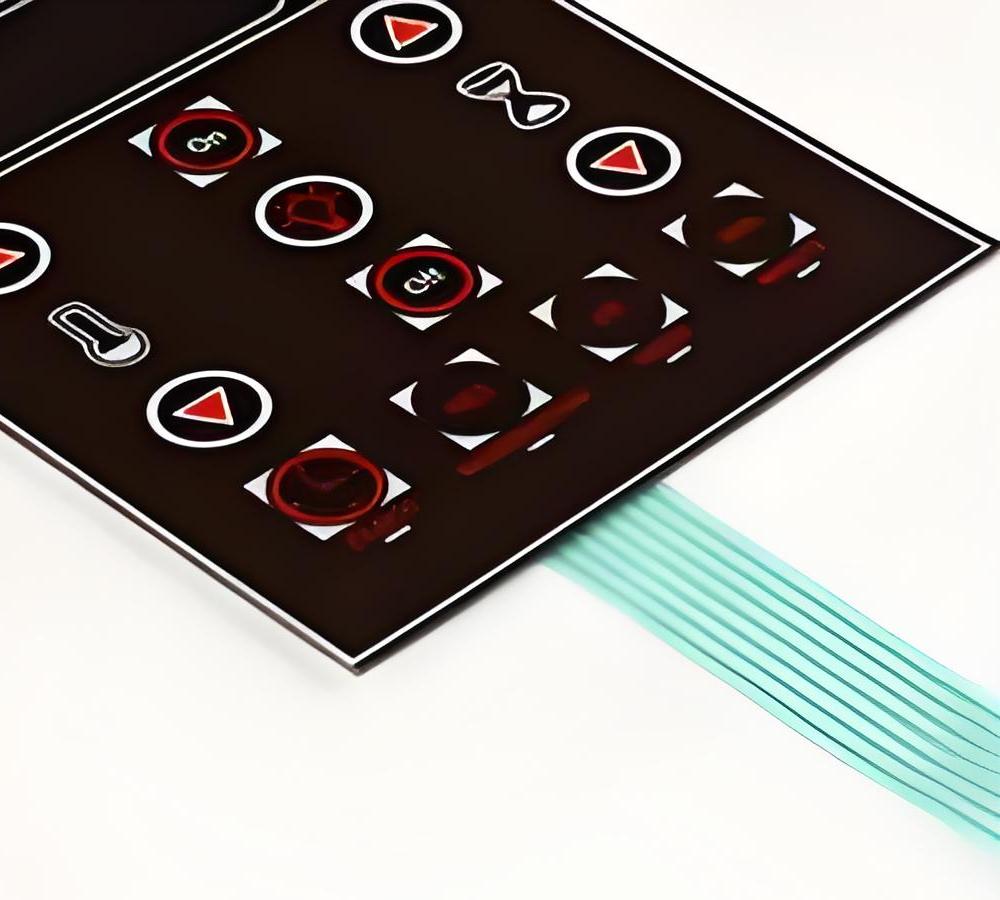
A membrane switch is electronic and non-mechanical. It uses printed circuits and pressure layers. There’s no lever. It’s activated through touch.
Let’s compare:
- Microswitch: Loud, clicky, mechanical parts, limited sealing, higher cost, compact size
- Membrane switch: Quiet, thin, sealed, flat, customizable, long-lasting
Microswitches are good for heavy-duty use. But they’re harder to seal and take up more space. Membrane switches are great for clean environments and user interfaces that need customization.
Nontactile membrane switches, in particular, outperform microswitches in quiet and sterile applications. They’re easier to integrate into modern touch systems.
Conclusion:
Nontactile membrane switch is a smart, flat, and silent solution for touch-based input. It doesn’t give physical feedback but offers lasting performance, easy cleaning, and seamless integration.
In high traffic, quiet or sanitary spaces, non-tactile membrane switches are the first choice. Its simple appearance and smooth touch make it the first choice for design.
Need help finding the perfect switch for your next product? Contact us now at sales@best-membraneswitch.com for samples, expert advice, or full support for your project.

Rubber Melting Temperature – Values for Common Rubber Types
Rubber is widely used in modern manufacturing because it offers flexibility, durability, and reliable performance under different conditions. Engineers rely on rubber materials for seals, keypads, insulation parts, and vibration control components. However, temperature performance is one of the most important properties to consider when selecting a rubber material for any product design. Many people ...

Backlit Membrane Switches – High-Quality Backlit Keypads
We provide reliable backlit membrane switches with long service life, stable backlight, and customizable design to fit your device control panel. What are backlit membrane switches? Backlit membrane switches are low-profile control interfaces that combine printed circuitry with integrated lighting. They allow users to see and operate equipment in low-light or dark environments. A backlit ...

Membrane Switch with LED, Customized LED Membrane Switches
Our LED membrane switches provide bright, even backlighting, long lifespan and reliable performance for control panels in dark environments. What are LED membrane switches? LED membrane switches are advanced user interface panels that combine a flexible membrane circuit with integrated light sources. The structure looks simple from the outside. Inside, it is a layered system ...
Contact us online