
What is a PCB membrane switch? Membrane PCBS
What is a PCB membrane switch? Membrane PCBS
PCB membrane switch have become essential in modern electronic devices. From industrial control panels to consumer gadgets, these switches offer a reliable and cost-effective interface. This blog dives deep into everything you need to know about membrane PCBS, their types, structure, functionality, and connection methods.

What is a PCB membrane switch?
A PCB membrane switch is a thin, flexible interface that connects human input to electronic circuits. Unlike traditional mechanical switches, membrane switches rely on a flexible printed circuit board (PCB) and a series of layers to detect key presses. They are designed for durability, space-saving, and ease of integration into compact devices.
Membrane PCBS combine simplicity and efficiency. Their low profile makes them ideal for devices where space is limited. They are resistant to dust, moisture, and dirt, which ensures reliable operation in various environments. Industries such as medical equipment, aerospace, and consumer electronics rely heavily on these switches for consistent performance.
What is a membrane key switch?
A membrane key switch is the user-facing part of a PCB membrane switch system. When you press a key on a membrane keypad, the switch beneath the surface completes an electrical circuit. This simple action triggers the device to respond.
Unlike conventional switches that rely on moving parts, membrane key switches use a flexible top layer to register input. This design eliminates wear-and-tear issues and reduces the need for regular maintenance.
Membrane key switches can be tactile or non-tactile. Tactile types provide a noticeable click or bump when pressed, giving users feedback, while non-tactile types operate silently. Both versions excel in compact designs, making them versatile for different applications.
What do membrane switches look like?
At first glance, a membrane switch appears as a flat, flexible surface with printed symbols, numbers, or graphics. Some have domed buttons that enhance tactile feedback. The top layer is usually made from polyester (PET) or polycarbonate, chosen for durability and flexibility.
Beneath the surface, membrane switches often contain a conductive layer and adhesive spacers. This design ensures that the circuit only closes when a button is pressed.
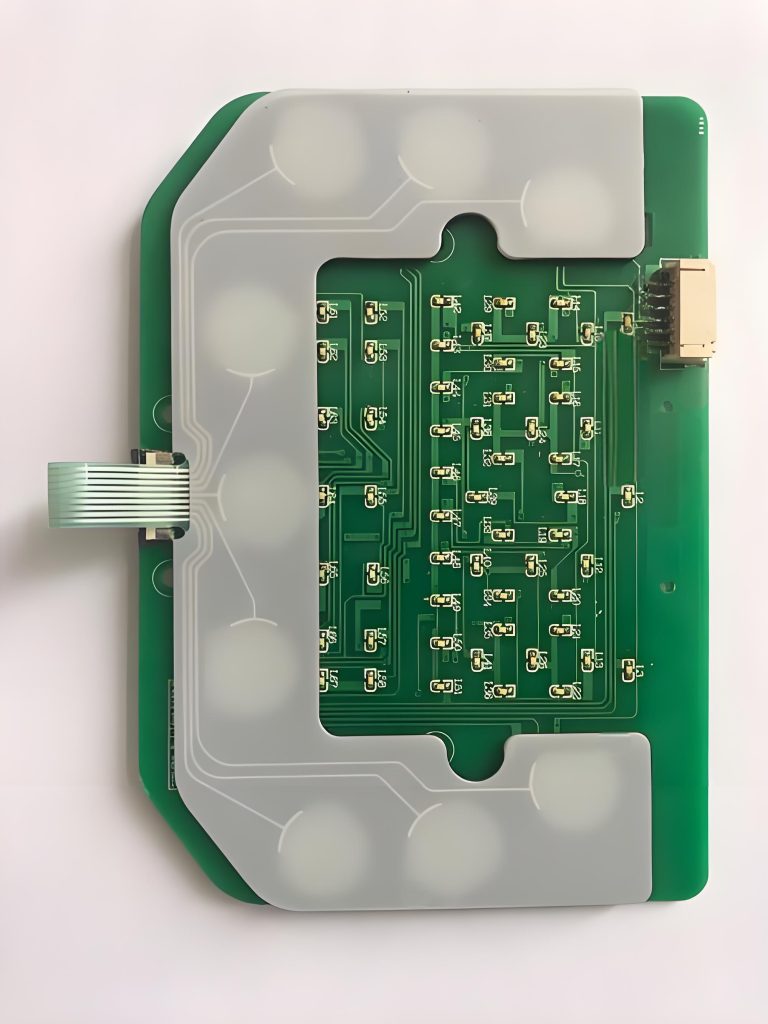
Visually, membrane PCBS are sleek and modern. They can be fully customized in color, texture, and graphics to match device aesthetics. Manufacturers often offer backlit options, improving visibility in low-light conditions.
This adaptability makes membrane switches appealing for consumer electronics, industrial controls, and medical devices.
What is the structure of a membrane switch?
A typical membrane switch consists of three main layers:
- Graphic Overlay: This is the topmost layer you see and touch. It features printed graphics, text, or symbols. It protects the internal components from external elements such as dust and moisture.
- Spacer Layer: This middle layer separates the top layer from the bottom conductive layer. It contains cut-outs where key presses occur, allowing the circuit to close only when pressed.
- Circuit Layer (PCB Layer): The bottom layer holds the conductive traces. When a key is pressed, the top layer contacts this conductive layer, completing the electrical circuit.
Some advanced designs include additional layers like:
- Backlighting layer for illuminating keys.
- Tactile dome layer for a responsive click.
- Adhesive layers to hold all components securely.
This multilayer construction allows membrane switches to remain thin, durable, and highly customizable.
What are the different types of PCB switches?
PCB switches come in several types, depending on the application and required feedback. Let’s explore the most common PCB switch types:
- 1. Tactile Membrane Switches
These switches provide a physical click or bump when pressed. They are common in appliances, calculators, and industrial control panels.
- 2. Non-Tactile Membrane Switches
These operate silently without physical feedback. Non-tactile switches are ideal for applications where noise must be minimized, such as medical or laboratory devices.
- 3. Surface Mount Tactile Membrane Switches
These are mounted directly onto the PCB using surface mount technology (SMT). They allow high-density layouts and automated assembly, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
- 4. Mechanical Switches on PCB
Sometimes, traditional mechanical switches are combined with a PCB interface. This hybrid design is less common but offers enhanced durability and feedback.
- 5. Capacitive Membrane Switches
These switches detect changes in capacitance rather than physical contact. Capacitive PCB membrane switches provide a sleek, touch-sensitive interface, often used in modern touch panels and smart devices.
Different applications dictate which switch type is chosen. For example, tactile membrane switches are favored in industrial environments for feedback, while capacitive types dominate consumer electronics for aesthetics and user experience.
How to connect switch to PCB?
Connecting a membrane switch to a PCB requires precision. Here’s how it’s generally done:
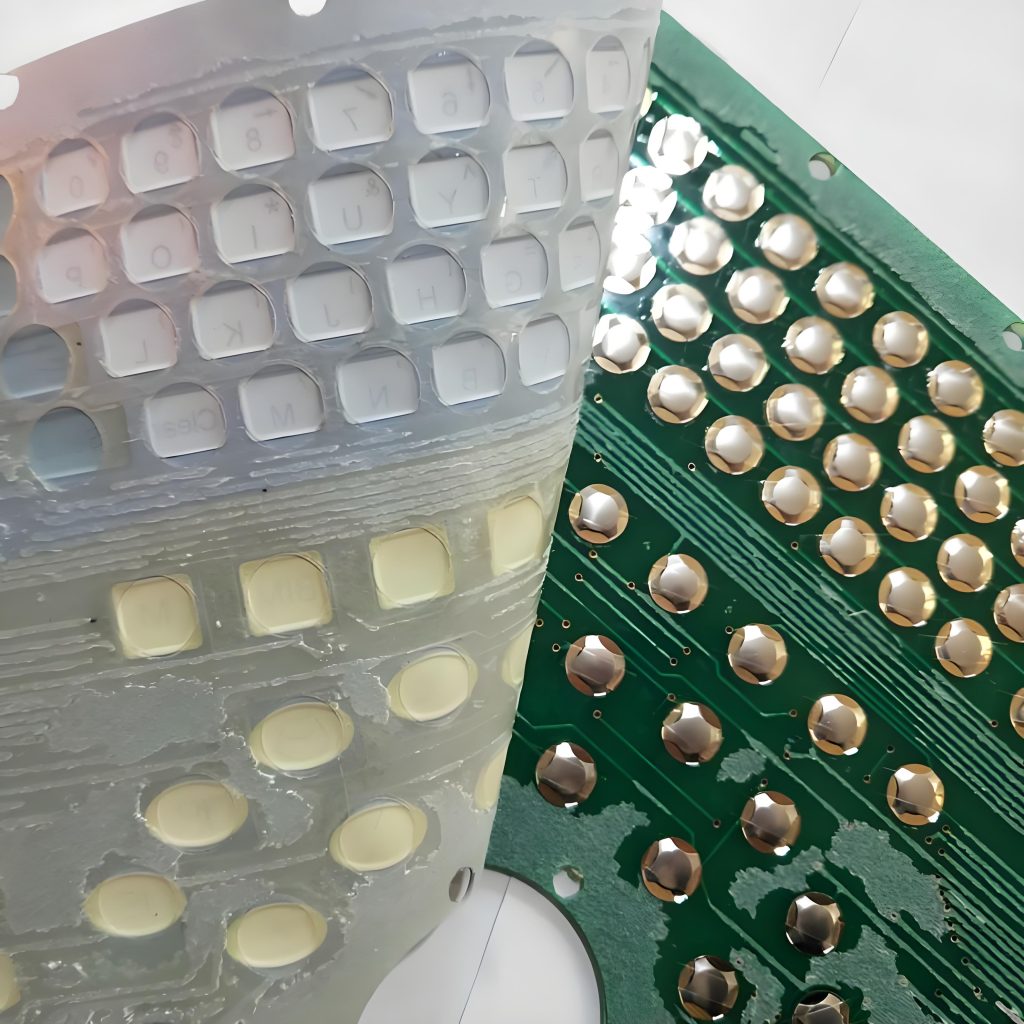
- Identify the Connector Type: Most membrane switches use a flexible tail with conductive traces. This tail fits into a membrane switch connector on the PCB.
- Align the Contacts: Carefully line up the contacts to ensure reliable conductivity. Misalignment can cause intermittent or failed connections.
- Secure the Connection: Depending on the design, connections may use ZIF (Zero Insertion Force) connectors, soldered pads, or adhesive conductive strips.
- Test the Circuit: Always verify that each key press completes the circuit properly. This step ensures functional reliability before assembly into the final device.

How do membrane switches work?
The working principle of a PCB membrane switch is simple yet effective. When a key is pressed:
- The top layer compresses and contacts the conductive circuit beneath.
- This closes the electrical circuit, sending a signal to the device.
- Releasing the key opens the circuit, ending the signal.
Tactile membrane switches often include a dome or bump, which snaps under pressure. This creates an audible and physical click. Non-tactile types rely solely on electrical closure, remaining silent.
Membrane switches are ideal for repetitive use. They endure thousands to millions of key presses without failure, making them highly reliable for long-term applications.
Are membrane switches swappable?
The question of swapability depends on the design. Most membrane PCBS are designed as single integrated units. This means individual keys are not easily swapped like mechanical switches.
However, some modular designs allow the entire keypad or certain sections to be replaced. This approach is common in industrial control panels or medical devices, where maintenance without complete replacement is desirable.
It’s important to note that attempting to replace individual keys in a standard membrane switch can damage the underlying circuit.
How long do membrane switches last?
Membrane switches are known for durability. High-quality membrane PCBS can withstand hundreds of thousands to millions of key presses. The lifespan depends on:
- Material quality: PET, polycarbonate, or specialized coatings enhance longevity.
- Switch type: Tactile domes may have slightly shorter life than non-tactile versions due to physical stress.
- Environmental conditions: Extreme moisture, dust, or temperature may reduce lifespan.
- Usage frequency: Higher use leads to faster wear, though membrane switches handle repeated use better than mechanical switches in most cases.
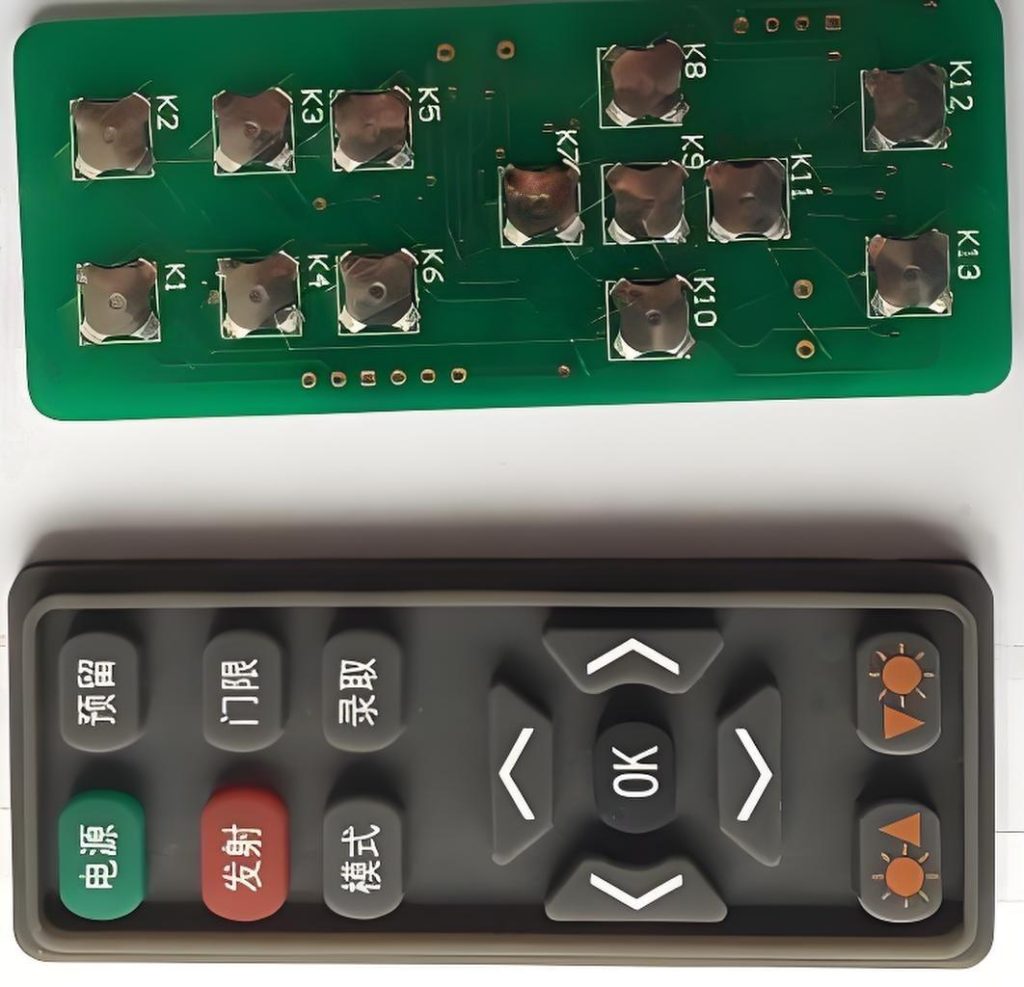
With proper design and manufacturing, PCB membrane switches can last years without noticeable degradation, offering excellent value for devices expected to operate over long periods.
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Can membrane switches be used in medical devices?
Yes, membrane PCBS are common in medical equipment due to their cleanliness, durability, and low maintenance requirements.
- 2. What is the difference between tactile and non-tactile switches?
Tactile switches give physical feedback, while non-tactile switches operate silently. The choice depends on user experience and application.
- 3. Can membrane switches support backlighting?
Absolutely. Backlit designs are common in consumer electronics and control panels for improved visibility.
- 4. How do I know which PCB switch type to choose?
Consider feedback, space, environment, and usage frequency. Tactile switches are ideal for frequent use; capacitive switches suit sleek touch interfaces.
- 5. Are membrane switch connectors standardized?
There are standard connector types like ZIF and FPC connectors.
Conclusion:
PCB membrane switches are an indispensable part of modern electronics. From tactile feedback to silent operation, membrane PCBS cater to diverse applications. Choosing the right switch type, understanding connection methods, and designing with quality materials ensures long-term reliability.
For engineers and manufacturers seeking high-quality membrane PCBS, Yu An Electronics offers custom solutions, professional guidance, and a commitment to excellence. Our expertise ensures every PCB switch meets rigorous standards for durability, performance, and user satisfaction.
For inquiries or custom solutions, contact sales@best-membraneswitch.com today.

Mechanical keyboard vs membrane: What’s the Difference?
When engineers and product teams compare mechanical keyboard vs membrane, they are usually deciding how users will interact with a device through a group of buttons. This decision affects reliability, feel, service life, sealing, and long-term maintenance. In industrial electronics, medical equipment, and embedded systems, the choice between a membrane keyboard and a mechanical keyboard ...
Silicone Rubber Keypad Manufacturer, Custom Membrane Switches
What is a silicone rubber keypad? Silicone rubber keypad is a flexible input component made from molded silicone elastomer. It allows users to press keys to send commands to an electronic device. Each key is formed as part of a single rubber sheet or pad. When pressed, the key makes contact with a circuit below ...

Custom Membrane Switches Manufacturers, Custom membrane switch panel
What Are Custom Membrane Switches? Custom membrane switches are thin, flexible, and highly adaptable electronic interfaces. They replace bulky mechanical keys and provide a lighter and more controlled input experience. These switches allow you to customize every part of the interface. You can choose the look, feel, shape, features, and layout. You can adjust the ...
Contact us online