
What is Printed Circuit Film(PCF) and how is it used in electronics
What is Printed Circuit Film(PCF) and how is it used in electronics
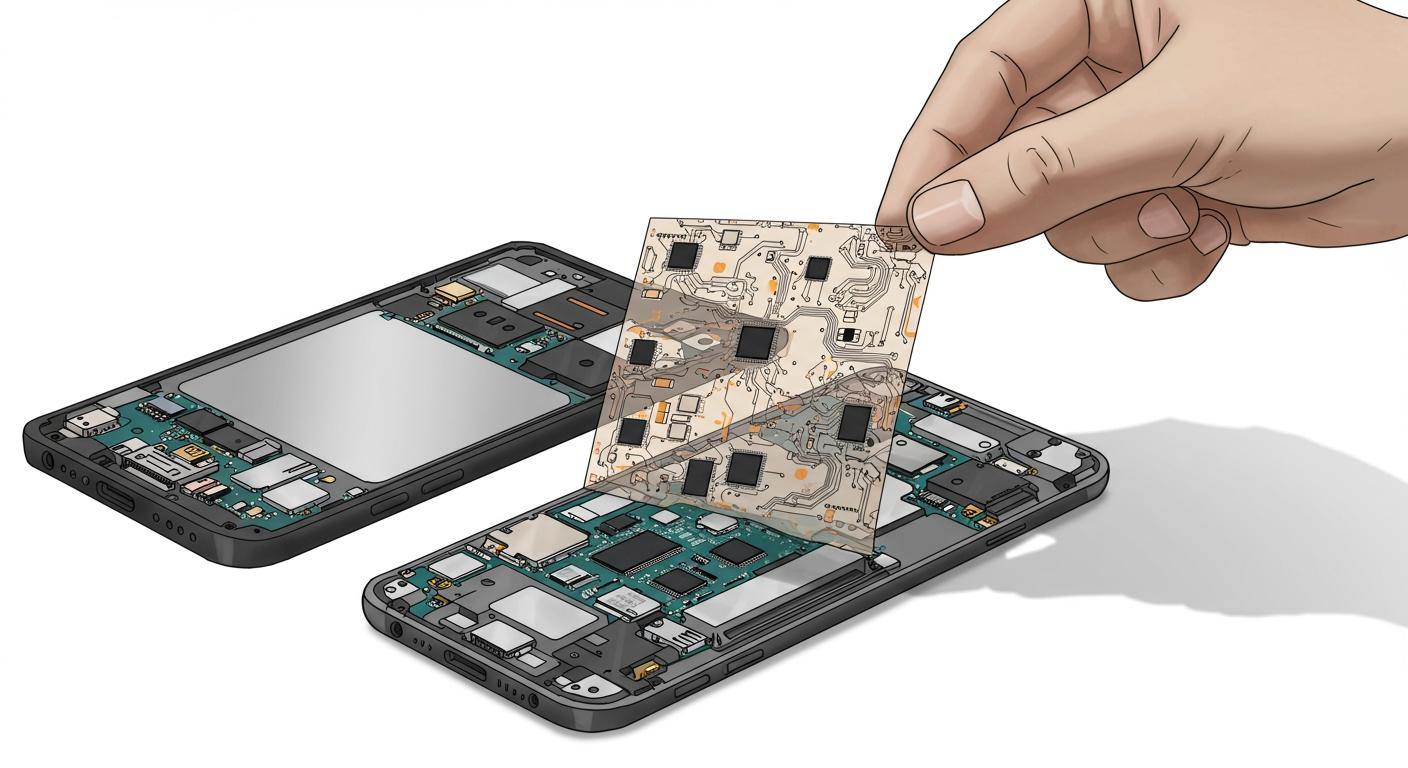
You rely on PCF-Printed Circuit Film to achieve precise circuit pattern transfer in advanced electronics. This specialized film offers extreme thinness and high photosensitivity, allowing you to create intricate designs on printed circuit boards. Its unique properties support high-density layouts essential for compact devices. When you work with space-constrained electronics, PCF-Printed Circuit Film ensures accuracy and efficiency in manufacturing.
Key Takeaways
- PCF-Printed Circuit Film is essential for creating precise and intricate circuit patterns in compact electronic devices.
- The film’s thinness and flexibility allow for high-density layouts, making it ideal for mobile phones, medical equipment, and automotive systems.
- Utilizing the photosensitive properties of PCF enables high-resolution designs, reducing the risk of errors during manufacturing.
- PCF offers advantages over traditional rigid PCBs, including greater flexibility and the ability to support complex wiring in tight spaces.
- Choosing the right materials for PCF can enhance device reliability and performance, especially in harsh environments.
Printed Circuit Film(PCF) Overview
Definition
You use PCF-Printed Circuit Film as a specialized material in the electronics industry. This film features a thin, flexible structure with high photosensitivity. You rely on it to transfer precise circuit patterns onto printed circuit boards. The film supports the creation of intricate and high-density layouts. Its unique properties make it essential for modern electronic devices that demand compactness and reliability.
Core Function
PCF-Printed Circuit Film serves as the backbone for transferring complex circuit designs onto substrates. You benefit from its ability to deliver accuracy and consistency during the manufacturing process. The film’s thinness and flexibility allow you to work with space-constrained devices. You find PCF-Printed Circuit Film especially valuable in applications that require lightweight and compact solutions.
- Mobile phones: You use the film to connect components like buttons and batteries, taking advantage of its lightweight and thin profile.
- Automobile systems: You design LED lights and engine control sensors with the film, ensuring reliable performance in demanding environments.
- Medical equipment: You create devices such as ultrasonic probes, where precision and miniaturization matter most.
- Robotics: You use the film as wiring for robot limbs, benefiting from its flexibility and durability.
- Computer and LCD screens: You rely on the film to convert digital signals into images, supporting high-resolution displays.
Note: You achieve greater design freedom and higher circuit density by choosing PCF-Printed Circuit Film for these advanced applications.
PCF Structure and Properties
Material Composition
You select the right material for PCF-Printed Circuit Film based on your application needs. The film uses advanced polymers and metals to deliver both flexibility and durability. You often work with polyester and polyimide, which provide a strong base for circuit patterns. Copper flex is another option that offers excellent conductivity and protection against oxidation. The table below shows the most common materials and their characteristics:
| Material Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Flexible Polyester | Commonly used, typically .002” to .005” thick, suitable for simple circuits with fewer components. |
| Polyimide | Used for more technical requirements, consists of a metallic layer bonded to a dielectric layer. |
| Copper Flex | Produced using photo or laser imaging, prevents oxidation with a protective layer. |
You choose these materials to ensure your circuits remain reliable and efficient, even in demanding environments.
Photosensitivity
You rely on the photosensitive nature of PCF-Printed Circuit Film to achieve precise circuit pattern transfer. The film responds to light exposure, allowing you to use photolithography for high-resolution designs. This process lets you create line widths and spacings as small as 0.1mm, which is essential for modern electronics. You also apply a photosensitive solder mask to protect your circuits and prevent short circuits. These features help you maintain accuracy and alignment throughout the manufacturing process.
- Dry film photolithography enables you to transfer circuit patterns with high precision.
- Photosensitive solder masks create protective layers, enhancing circuit alignment and reliability.
Tip: You can achieve intricate designs and avoid costly errors by leveraging the photosensitive properties of PCF-Printed Circuit Film.
Thinness and Density
You benefit from the thin and dense structure of PCF-Printed Circuit Film when designing compact devices. The film’s ultra-thin profile allows you to stack multiple layers, reducing the overall height of your electronic package. You find this especially useful for mobile devices and wearables, where space is limited. The lightweight nature of the film makes it ideal for applications that require portability. You also gain mechanical strength and flexibility, which support advanced packaging solutions like flip-chip bonding. Enhanced thermal dissipation helps you manage heat in high-performance electronics.
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Thinness | Enables ultra-thin, high-density laminates, reducing overall package height. |
| Lightweight | Ideal for mobile devices and wearables where space is constrained. |
| Mechanical Strength | Provides durability and reliability in compact designs. |
| Flexibility | Allows for advanced packaging solutions like flip-chip bonding. |
| Enhanced Thermal Dissipation | Improves thermal performance, essential for high-performance electronics. |
You achieve greater circuit density and reliability by choosing PCF-Printed Circuit Film for your high-density, space-constrained designs.
Printed Circuit Film (PCF) vs. Other Technologies
Rigid PCBs Comparison
You often work with rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs) when you need strong, inflexible support for your electronic components. Rigid PCBs use fiberglass or epoxy as their base material. These boards provide excellent mechanical stability. However, you face limitations with rigid PCBs in compact or curved designs. You cannot bend or flex them without causing damage. PCF-Printed Circuit Film offers you a solution for applications that require thin, lightweight, and flexible circuits. You achieve higher circuit density and better space utilization with PCF compared to rigid PCBs.
Flexible Circuits Comparison
You choose flexible circuits when you need to fit electronics into tight or irregular spaces. Flexible circuits use polyimide or polyester substrates, similar to PCF. You can bend, twist, or fold these circuits without losing performance. PCF gives you even greater precision in pattern transfer due to its photosensitive properties. You create more intricate designs and achieve finer line widths with PCF. Flexible circuits work well for wearable devices, medical sensors, and foldable displays. PCF enhances these applications by supporting higher density and improved reliability.
Advantages and Limitations
You gain several advantages by using PCF-Printed Circuit Film:
- You achieve ultra-thin and lightweight designs.
- You transfer complex patterns with high accuracy.
- You support high-density layouts for advanced electronics.
- You improve thermal management in compact devices.
However, you should consider some limitations:
- You may face higher material costs for specialized films.
- You need precise manufacturing controls to avoid defects.
- You may encounter challenges with mechanical strength in extreme environments.
Note: You should evaluate your application requirements before choosing PCF. You maximize performance and reliability when you match the technology to your design needs.
| Technology | Flexibility | Density | Cost | Application Scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rigid PCB | Low | Medium | Moderate | Standard electronics |
| Flexible Circuit | High | High | Moderate | Wearables, sensors |
| PCF | Very High | Very High | Higher | High-density, compact |
Applications
Consumer Electronics
You see PCF-Printed Circuit Film driving innovation in consumer electronics. You use this technology to create thinner smartphones, tablets, and wearables. The film allows you to design compact circuit layouts that fit inside slim devices. You achieve higher circuit density, which supports advanced features like touchscreens and high-resolution displays. You also benefit from improved durability and flexibility, making your devices more reliable for everyday use.
- The market for electronic thick film pastes reached about USD 2.5 billion in 2023.
- You expect this market to grow to nearly USD 4.8 billion by 2032, with a 7.1% CAGR.
- Rising demand in consumer electronics fuels this growth.
Tip: You can deliver more powerful and feature-rich products by leveraging PCF-Printed Circuit Film in your designs.
Automotive Systems
You rely on PCF-Printed Circuit Film to meet the demands of modern automotive systems. You use it in LED lighting, engine control units, and advanced driver-assistance systems. The film’s thin profile lets you fit circuits into tight spaces, such as dashboards and sensor modules. You achieve high reliability and resistance to harsh conditions, which is essential for vehicles. You also support complex wiring layouts that enable smart features and connectivity.
- Automotive manufacturers use PCF to improve safety and performance.
- You see increased adoption in electric vehicles and autonomous driving technologies.
Note: You can enhance vehicle functionality and safety by integrating PCF-Printed Circuit Film into automotive electronics.
Telecommunications
You play a key role in telecommunications by using PCF-Printed Circuit Film for high-performance equipment. The film supports complex and high-density circuit designs needed for fast data transmission and reliable communication. You find PCF essential in fiber-optic networks, laser systems, and sensitive sensors.
| Application Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Fiber-optic communications | Utilizes PCF for efficient data transmission over long distances. |
| Fiber lasers | PCF enhances the performance of lasers used in various applications. |
| Nonlinear devices | Enables advanced functionalities in devices that rely on nonlinear optics. |
| High-power transmission | Supports the transmission of high power signals without loss. |
| Highly sensitive gas sensors | Improves sensitivity and accuracy in detecting gas concentrations. |
You support the rapid growth of telecommunications by adopting PCF-Printed Circuit Film. You enable faster, more reliable networks and advanced sensing capabilities.
You now understand how PCF-Printed Circuit Film shapes modern electronics. This film gives you the tools to create precise, high-density circuits for compact devices. You see its advantages over rigid and flexible boards in many industries. By learning about its structure and uses, you prepare yourself for future innovation in electronics.
Stay informed about PCF-Printed Circuit Film to lead in advanced circuit design.
FAQ
What makes PCF-Printed Circuit Film different from traditional PCBs?
You use PCF-Printed Circuit Film for its thin, flexible, and photosensitive properties. These features allow you to create high-density circuits in compact devices. Traditional PCBs lack this flexibility and cannot support such intricate designs.
Can you recycle PCF-Printed Circuit Film?
You can recycle some PCF materials, especially those based on polyimide or polyester. However, you need specialized recycling processes to separate metals from polymers. Always check local recycling guidelines before disposal.
Tip: Contact your supplier for recycling options specific to your PCF material.
How does PCF improve device reliability?
You benefit from PCF’s precise pattern transfer and strong material composition. These qualities reduce the risk of short circuits and mechanical failure. You achieve longer device lifespans and fewer malfunctions.
Where do you see PCF-Printed Circuit Film most often?
You find PCF in smartphones, automotive sensors, medical devices, and telecommunications equipment. These industries require compact, high-density, and reliable circuit solutions.
| Industry | Common Use Case |
|---|---|
| Consumer Tech | Smartphones, wearables |
| Automotive | Sensors, lighting |
| Medical | Probes, monitors |
| Telecom | Fiber optics, sensors |
Is PCF suitable for harsh environments?
You can use PCF in harsh environments if you select the right material. Polyimide-based films offer excellent heat and chemical resistance. Always match your PCF choice to your application’s demands.

Capacitive Touch Switch – Reliable for Smart Device Control
Need professional capacitive touch switch solutions? We provide durable, customizable touch switches for all electronic control panels with stable performance. What is capacitive switching? Capacitive switching is a control method based on the electrical behavior of the human body. When a finger approaches or touches a sensing area, it changes the local electric field. The ...

Mechanical keyboard vs membrane: What’s the Difference?
When engineers and product teams compare mechanical keyboard vs membrane, they are usually deciding how users will interact with a device through a group of buttons. This decision affects reliability, feel, service life, sealing, and long-term maintenance. In industrial electronics, medical equipment, and embedded systems, the choice between a membrane keyboard and a mechanical keyboard ...
Silicone Rubber Keypad Manufacturer, Custom Membrane Switches
What is a silicone rubber keypad? Silicone rubber keypad is a flexible input component made from molded silicone elastomer. It allows users to press keys to send commands to an electronic device. Each key is formed as part of a single rubber sheet or pad. When pressed, the key makes contact with a circuit below ...
Contact us online