
Backlit vs Edge Light for Membrane Switches
Backlit vs Edge Light for Membrane Switches
When designing a user interface, lighting can make all the difference. Whether it’s a piece of medical equipment, a control panel in a factory, or the dashboard of a smart appliance, membrane switch lighting creates a better experience for the user. Two popular options, backlit membrane switches and edge-lit membrane switches, offer unique ways to light up control panels. Choosing between them isn’t just about appearance — it affects usability, cost, durability, and performance. This guide dives deep into backlit vs edge light membrane switches, helping engineers, designers, and buyers make informed decisions that fit their specific needs.
What is a Backlit Membrane Switch?
A backlit membrane switch is an illuminated control panel that uses lights placed directly underneath the graphic overlay. Light shines through the design elements, making symbols, text, or backgrounds visible even in the dark. This type of membrane switch creates a clean, modern look that improves functionality and branding.
These switches often rely on LEDs, fiber optics, or electroluminescent panels. Each option provides different benefits depending on the product requirements. For industries like medical devices or aerospace, where precision and reliability matter, backlit membrane switches offer clear visibility without compromising panel thinness.

How Does Backlit Membrane Switches Work?
The working principle of backlit membrane switches is based on membrane electronics and is typically used for backlight module control in electronic devices. A backlit membrane switch mainly consists of two transparent conductive film layers, with a transparent pressure-sensitive material sandwiched between them. When slight pressure is applied, the pressure-sensitive material deforms and contacts the conductive films, forming a closed circuit that turns the backlight on or off.
When a user gently touches or presses the switch, the pressure-sensitive material deforms, the conductive layers come into contact, the circuit closes, and the backlight is controlled accordingly.
Advantages of Backlit Membrane Switches
- Low Power Consumption: By controlling the circuit switch, energy is effectively conserved.
- Low Noise: No mechanical noise during operation.
- Long Lifespan: Due to material selection and proper design, membrane switches can endure a high number of operations without deformation, ensuring a long service life.
- Easy Integration: Thanks to their simple structure, they can be easily integrated into other electronic devices.
However, backlit membrane switches also have some limitations:
- Limited Application Range: Primarily suitable for scenarios requiring backlight control, such as keypad backlighting in electronic devices.
- Technical Requirements: Precise manufacturing processes and material selection are needed to ensure reliability and durability.
Common Backlighting Methods Used Today
- LED Backlighting: Offers strong brightness, long lifespan, and flexible design options. Perfect for detailed graphics or variable brightness needs.
- Electroluminescent (EL) Panels: Produce uniform, low-glare light across large areas. Ideal for soft, consistent illumination but typically have shorter lifespans than LEDs.
- Fiber Optic Lighting: Channels light precisely where needed without extra bulk. Works well for designs needing multiple isolated illuminated zones.
- Light Guide Film (LGF): Distributes LED light efficiently across wide surfaces while keeping the switch profile extremely thin.

What is an Edge-Lit Light Membrane Switch?
An edge-lit membrane switch takes a different approach. Instead of shining light through the entire panel from behind, LEDs are placed around the border. Light enters a special light guide layer and travels across the panel through internal reflection.

When the light meets textured or etched surfaces within the panel, it scatters outward, becoming visible to the user. This method highlights specific elements while keeping most of the panel surface dark, often used in high-end industrial controls, medical devices, and consumer electronics.
How Edge-Lit Technology Functions in Membrane Interfaces?
In edge-lit membrane switches, the key lies in controlling how light moves and where it escapes. LEDs inject light into a clear or semi-clear substrate. Patterns or micro-structures within the layer guide the light and create intentional breakout points where illumination appears.
The design process involves choosing the right materials for clarity and reflectivity. The number and placement of LEDs affect how bright and even the final illumination appears. Edge-lighting provides lower power consumption compared to full backlighting, especially useful when designing battery-operated or energy-sensitive devices.
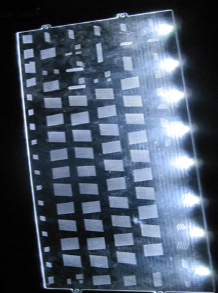
Key Differences Between Backlit vs Edge Light Membrane Switches
- Illumination Area: Backlit switches light up the full button, symbol, or panel, while edge-lit designs create selective highlights.
- Brightness Style: Backlit designs produce soft, full-field glow; edge-lit models offer sharper, focused lighting effects.
- Energy Usage: Edge-lighting often uses fewer LEDs, saving power over time.
- Design Complexity: Backlighting can support complex, multi-color graphics. Edge-lighting suits sleek, simplified layouts.
- Cost Factors: Edge-lit switches generally require fewer components, which may lower costs.
- Panel Thickness: Both designs can be made slim, but edge-lit systems allow ultra-thin profiles more easily.
- Actuation Force: Well-designed backlit panels maintain comfortable pressing force despite extra lighting layers.
Considerations When Designing Backlit Membrane Switch Panels
Designing a backlit panel demands careful planning. Here are some basic design guides of backlit membrane switch:
- Material Transparency: Clear and semi-transparent layers must transmit enough light without washing out the colors or graphics.
- LED Placement: LEDs generate some heat, even spacing prevents hotspots or dim zones, critical for professional appearance.
- Durability: Outdoor or rugged applications require protective coatings or UV-resistant materials to preserve lighting clarity over time.
- Surface protection layer: The surface protection layer is anti-glare/anti-fingerprint treated with a thickness of 0.125-0.2mm.
- Circuit layer: The circuit layer uses silver paste or carbon paste conductive lines with a thickness of 0.05-0.1mm.
- Spacer layer: The spacer layer is cut with pores by precision laser, with a thickness of 0.1-0.3mm.
- Back glue layer: The back glue layer needs to have high temperature resistance, with a temperature range of -40℃ to +85℃.
- Waterproof and oil-proof design: Membrane switches used in humid environments such as bathroom equipment need to have IP67 waterproof design and be able to maintain a stable key life in high humidity environments.
- Antibacterial design: In medical-grade home appliances, antibacterial coatings can achieve an antibacterial rate of 99.9%, improving hygiene standards.
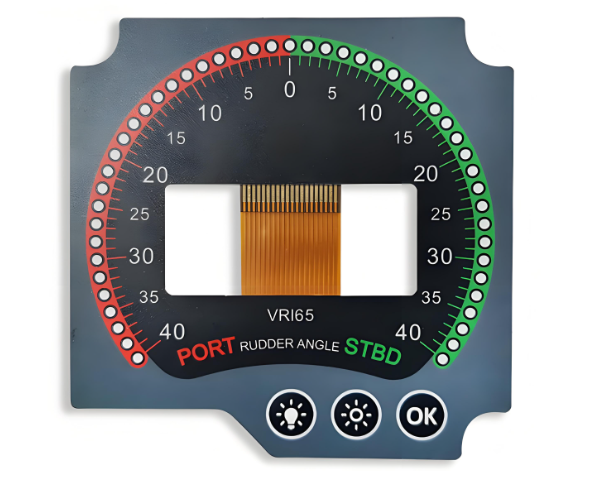
Applications of Membrane Switches
Membrane switches, especially those with backlit or edge-lit lighting, serve critical roles across industries:
- Medical Equipment
- Industrial Controls
- Consumer Electronics
- Household Appliances
- Communications
- Automotives
- Human Machine Interface (HMI)
- Intelligent Toys
- Transportation Systems
- Military and Defense Gear
FAQs
1. Can you get custom colors with membrane switch lighting?
Absolutely. Both LED color choices and graphic printing techniques enable fully customized branding and design expressions.
2. Can a membrane switch combine backlighting and edge-lighting?
Yes. Hybrid designs allow creative layouts where main areas glow softly and key features pop with sharper edge illumination.
3. Which lighting method offers a thinner membrane switch?
Edge-lighting typically leads to slimmer profiles without sacrificing durability or brightness.
4. What lifespan can be expected from the lights in membrane switches?
LEDs often last more than 50,000 hours, supporting years of dependable operation. Electroluminescent panels offer a solid 10,000–20,000 hours.
Tactile Dome Switch – For Electronics & Control Panel Design
Our tactile dome switch delivers crisp tactile feedback and reliable precision actuation, with industrial-grade durability for small device control panels. Custom sizes available for your design needs. What is a tactile dome switch? A tactile dome switch is a compact switching component used in electronic interfaces where clear feedback matters. It delivers a sharp, physical ...

Custom Membrane Keypads – Industrial Grade Custom Design
Our custom membrane keypads are engineered with industrial-grade durability, waterproof & oil-resistant for control panels. Fully customizable sizes, layouts and symbols for your device needs. What is a custom membrane keypad? A custom membrane keypad is a low-profile input interface designed for a specific product, device, or operating environment. It combines printed circuits, tactile layers, ...

What is a membrane switch dome? China metal dome membrane switch
A membrane switch dome is a small but powerful part of many modern input devices. You see it in factory control panels, medical tools, handheld devices, POS systems, and more. It looks simple, yet it shapes how a product feels, responds, and lasts over time. What Is a Dome Switch Membrane Keyboard? A dome switch ...
Contact us online